England’s First “Black” Queen, Was Really Bi-racial, Sophie Charlotte Born 1744
by Kathy Grear 05/21/2018First Black (mixed-race) Queen of England - Continued
Contents
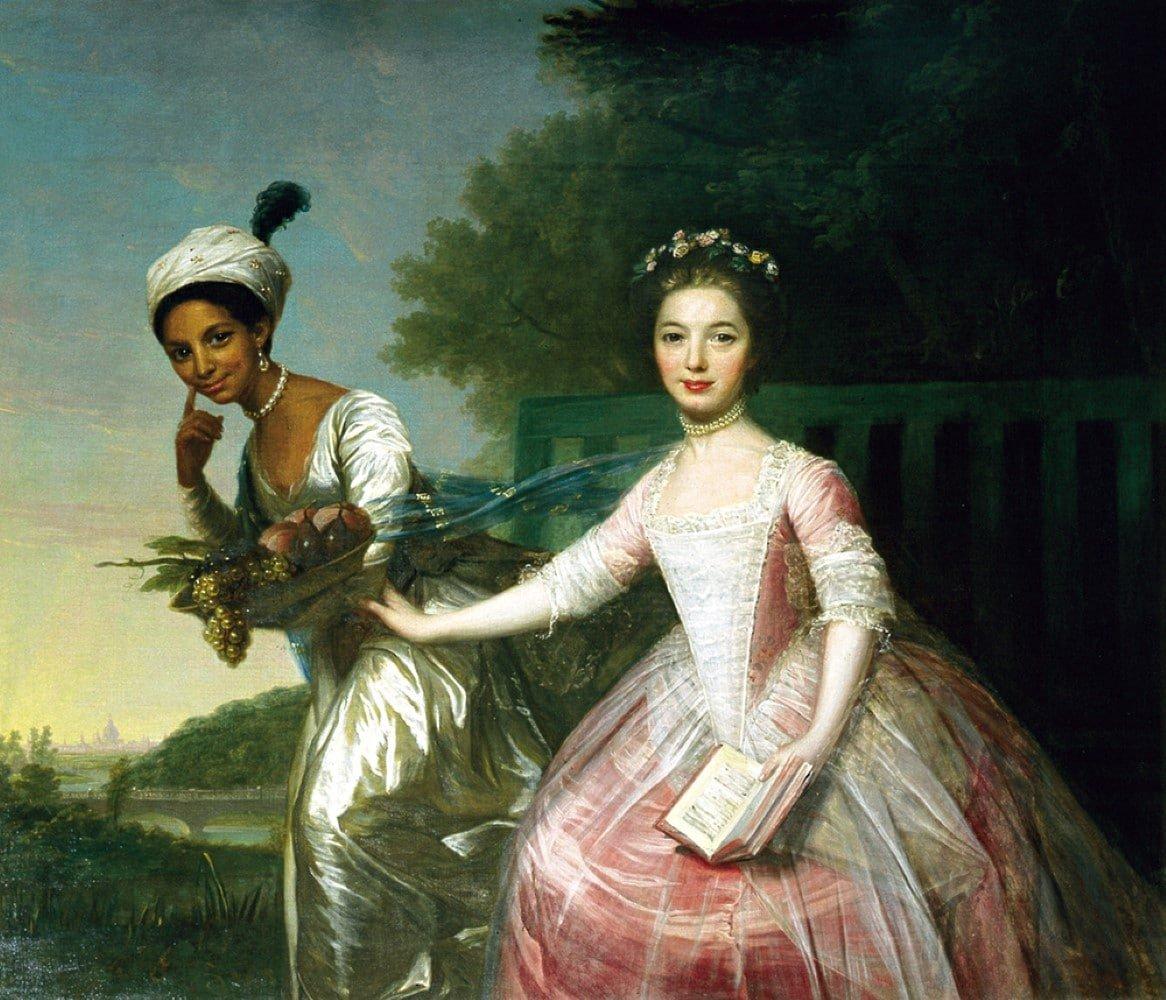
Dido Elizabeth Belle and the Lady Elizabeth Murray “Dido” Elizabeth Belle was a bi-racial woman born into slavery in 1761 in the West Indies, the daughter of a slave woman, Maria Belle
Lord Mansfield’s black grand niece, for example, Ms. Lindsay, was the subject of at least two formal full sized portraits. Obviously prompted by or meant to appeal to abolitionist sympathies, they depicted the celebrated friendship between herself and her white cousin, Elizabeth Murray, another member of the Mansfield family. One of the artists was none other than Zoffany, the court painter to the royal family, for whom the First Black Queen of England had sat on a number of occasions.
It is perhaps because of this fairly obvious case of propagandistic portraiture that makes one suspect that Queen Charlotte’s coronation picture, copies of which were sent out to the colonies, signified a specific stance on slavery held, at least, by that circle of the English intelligencia to which Allan Ramsay, the painter belonged.
More on First Black Queen of England
- Revealed: the Queen’s black ancestors
The Times of London reports that a Portuguese descendent of Queen Charlotte confirmed Valdes’ research into her heritage. (June 6, 1999)
- Was this Britain’s first black queen?
“The suggestion that Queen Charlotte was black implies that her granddaughter (Queen Victoria) and her great-great-great-great-granddaughter (Queen Elizabeth II) had African forebears. Perhaps, instead of just being a boring bunch of semi-inbred white stiffs, our royal family becomes much more interesting.” (The Guardian, March 12, 2009)
For the initial work into Queen Charlotte’s genealogy, a debt of gratitude is owed the History Department of McGill University. It was the director of the Burney Project (Fanny Burney, the prolific 19th century British diarist, had been secretary to the Queen), Dr. Joyce Hemlow, who obtained from Olwen Hedly, the most recent biographer of the Queen Charlotte (1975), at least half a dozen quotes by her contemporaries regarding her negroid features. Because of its “scientific” source, the most valuable of Dr. Hedley’s references would, probably, be the one published in the autobiography of the Queen’s personal physician, Baron Stockmar, where he described her as having “…a true mulatto face.”
Perhaps the most literary of these allusions to her African appearance, however, can be found in the poem penned to her on the occasion of her wedding to George III and the Coronation celebration that immediately followed.
Descended from the warlike Vandal race,
She still preserves that title in her face.
Tho’ shone their triumphs o’er Numidia’s plain,
And and Alusian fields their name retain;
They but subdued the southern world with arms,
She conquers still with her triumphant charms,
O! born for rule, – to whose victorious brow
The greatest monarch of the north must bow.
Finally, it should be noted that the Royal Household itself, at the time of Queen Elizabeth II’s coronation, referred to both her Asian and African bloodlines in an apologia it published defending her position as head of the Commonwealth.
More about Research into the Black Magi:
In the Flemish masterpieces depicting the Adoration of the Magi, the imagery of the black de Sousas had been utilized as both religious and political propaganda to support Portugal’s expansion into Africa. In addition, the Flemish artists had drawn from a vocabulary of blackness which, probably due to the Reformation and the Enlightenment, has long since been forgotten. There was a wealth of positive symbolism that had been attributed to the black African figure during the Middle Ages. Incredible as it would seem to us today, such images had been used to represent not only Our Lady – evidence of which can be found in the cult of the Black Madonna that once proliferated in Europe – but in heraldic traditions, the Saviour and God the Father, Himself.


